| APAF1 |
|---|
 |
|
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
1C15, 1CWW, 1CY5, 1Z6T, 2P1H, 2YGS, 3J2T, 3YGS, 4RHW, 3JBT |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | APAF1 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 602233 MGI: 1306796 HomoloGene: 7626 GeneCards: APAF1 |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 12q23.1 | Début | 98,645,290 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 98,735,433 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 10 C2|10 45.47 cM | Début | 90,989,311 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 91,082,770 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
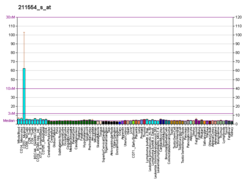
| Fortement exprimé dans | - monocyte
- ventricular zone
- sang
- cellule de la moelle osseuse
- éminence ganglionnaire
- epithelium of colon
- granulocyte
- tendon calcanéen
- os spongieux
- testicule
|
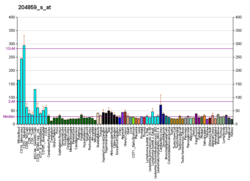
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - granulocyte
- derme
- migratory enteric neural crest cell
- uretère
- Jéjunum
- canal déférent
- otic vesicle
- stroma of bone marrow
- gastrula
- iléon
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - heat shock protein binding
- ADP binding
- liaison protéique
- identical protein binding
- liaison ATP
- liaison nucléotide
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process
| | Composant cellulaire | - cytoplasme
- cytosol
- exosome
- noyau
- apoptosome
- région extracellulaire
- secretory granule lumen
- ficolin-1-rich granule lumen
- complexe macromoléculaire
| | Processus biologique | - cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus
- neuron apoptotic process
- regulation of apoptotic process
- différenciation cellulaire
- response to hypoxia
- response to nutrient
- response to G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling
- vieillissement
- positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway
- glial cell apoptotic process
- neurodéveloppement
- développent d'un organisme multicellulaire
- cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
- neural tube closure
- développement cérébral
- positive regulation of apoptotic process
- apoptotic signaling pathway
- forebrain development
- regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation
- protein homooligomerization
- activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process by cytochrome c
- apoptose
- neutrophil degranulation
- negative regulation of G0 to G1 transition
- kidney development
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001160
NM_013229
NM_181861
NM_181868
NM_181869 |
| |
|---|
NM_001042558
NM_001282947
NM_009684 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | |
|---|
NP_001151
NP_037361
NP_863651
NP_863658
NP_863659 |
| |
|---|
NP_001036023
NP_001269876
NP_033814 |
|
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 12: 98.65 – 98.74 Mb | Chr 10: 90.99 – 91.08 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|

 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biochimie
Portail de la biochimie  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire