AM-251 (drug)
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| IUPHAR/BPS |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.062 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H21Cl2IN4O |
| Molar mass | 555.24 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
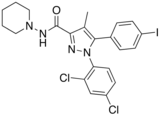
AM-251 is an inverse agonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. AM-251 is structurally very close to rimonabant; both are biarylpyrazole cannabinoid receptor antagonists. In AM-251, the p-chloro group attached to the phenyl substituent at C-5 of the pyrazole ring is replaced with a p-iodo group. The resulting compound exhibits slightly better binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (with a Ki value of 7.5 nM) than rimonabant, which has a Ki value of 11.5 nM, AM-251 is, however, about two-fold more selective for the CB1 receptor when compared to rimonabant.[1] Like rimonabant, it is additionally a μ-opioid receptor antagonist[2] that attenuates analgesic effects.[3]
AM251 has shown an in vitro antimelanoma activity against pancreatic and colon cancer cells.[4]
See also
References
- ^ Lan R, Liu Q, Fan P, Lin S, Fernando SR, McCallion D, et al. (February 1999). "Structure-activity relationships of pyrazole derivatives as cannabinoid receptor antagonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 42 (4): 769–776. doi:10.1021/jm980363y. PMID 10052983.
- ^ Seely KA, Brents LK, Franks LN, Rajasekaran M, Zimmerman SM, Fantegrossi WE, Prather PL (October 2012). "AM-251 and rimonabant act as direct antagonists at mu-opioid receptors: implications for opioid/cannabinoid interaction studies". Neuropharmacology. 63 (5): 905–915. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.046. PMC 3408547. PMID 22771770.
- ^ Seely KA, Brents LK, Franks LN, Rajasekaran M, Zimmerman SM, Fantegrossi WE, Prather PL (October 2012). "AM-251 and rimonabant act as direct antagonists at mu-opioid receptors: implications for opioid/cannabinoid interaction studies". Neuropharmacology. 63 (5): 905–915. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.046. PMC 3408547. PMID 22771770.
- ^ Carpi S, Fogli S, Romanini A, Pellegrino M, Adinolfi B, Podestà A, et al. (August 2015). "AM251 induces apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest in A375 human melanoma cells" (PDF). Anti-Cancer Drugs. 26 (7): 754–762. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000246. hdl:11568/750318. PMID 25974027. S2CID 205526223. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 2, 2021.
- v
- t
- e
(comparison)
| Cannabibutols |
|
|---|---|
| Cannabichromenes | |
| Cannabicyclols |
|
| Cannabidiols | |
| Cannabielsoins |
|
| Cannabigerols | |
| Cannabiphorols |
|
| Cannabinols | |
| Cannabitriols |
|
| Cannabivarins |
|
| Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinols |
|
| Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinols | |
| Delta-10-Tetrahydrocannabinols | |
| Miscellaneous cannabinoids |
|
| Active metabolites |
- Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide)
- 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
- 2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether (2-AGE; noladin ether)
- 2-Oleoylglycerol (2-OG)
- N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA)
- N-Arachidonylglycine (NAGly)
- 2-Arachidonoyl lysophosphatidylinositol (2-ALPI)
- N-Arachidonoyl serotonin (AA-5-HT)
- Docosatetraenoylethanolamide (DEA)
- Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI)
- Oleamide
- Oleoylethanolamide (OEA)
- Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)
- RVD-Hpα
- Stearoylethanolamide (SEA)
- O-Arachidonoyl ethanolamine (O-AEA; virodhamine)
cannabinoid
receptor
agonists /
neocannabinoids
| Classical cannabinoids (dibenzopyrans) |
|
|---|---|
| Non-classical cannabinoids |
|
| Adamantoylindoles |
|
| Benzimidazoles | |
| Benzoylindoles |
|
| Cyclohexylphenols | |
| Eicosanoids |
|
| Hydrocarbons | |
| Indazole carboxamides | |
| Indazole-3- carboxamides |
|
| Indole-3-carboxamides |
|
| Indole-3-carboxylates | |
| Naphthoylindazoles | |
| Naphthoylindoles |
|
| Naphthoylpyrroles | |
| Naphthylmethylindenes | |
| Naphthylmethylindoles | |
| Phenylacetylindoles | |
| Pyrazolecarboxamides |
|
| Pyrrolobenzoxazines | |
| Quinolinyl esters | |
| Tetramethylcyclo- propanoylindazoles | |
| Tetramethylcyclo- propanoylindoles | |
| Tetramethylcyclo- propylindoles | |
| Others |
|
enhancers
(inactivation inhibitors)
- 4-Nonylphenylboronic acid
- AM-404
- Arachidonoyl serotonin
- Arvanil
- BIA 10-2474
- Biochanin A
- CAY-10401
- CAY-10429
- Genistein
- Guineesine
- IDFP
- JNJ 1661010
- JNJ-42165279
- JZL184
- JZL195
- Kaempferol
- LY-2183240
- MK-4409
- O-1624
- O-2093
- Oleoylethanolamide (OEA)
- Olvanil
- Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)
- PF-04457845
- PF-622
- PF-750
- PF-3845
- PHOP
- URB-447
- URB-597
- URB-602
- URB-754
- VDM-11
(antagonists/inverse
agonists/antibodies)
- AM-251
- AM-281
- AM-630
- AM-1387
- AM-4113
- AM-6527
- AM-6545
- BML-190
- Brizantin (Бризантин)
- CAY-10508
- CB-25
- CB-52
- CB-86
- Dietressa (Диетресса)
- Drinabant (AVE1625)
- Hemopressin
- Ibipinabant (SLV319)
- JTE-907
- LH-21
- LY-320,135
- MDA-77
- MJ-15
- MK-9470
- NESS-0327
- NIDA-41020
- O-606
- O-1184
- O-1248
- O-1918
- O-2050
- O-2654
- Otenabant (CP-945,598)
- PF-514273
- PipISB
- PSB-SB-487
- Rimonabant (SR141716)
- Rosonabant (E-6776)
- SR-144,528
- Surinabant (SR147778)
- Taranabant (MK-0364)
- TM-38837
- VCHSR
- See also: Cannabinoid receptor modulators (cannabinoids by pharmacology)
- List of: AM cannabinoids
- JWH cannabinoids
- Designer drugs § Synthetic cannabimimetics
 | This cannabinoid related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e













