Thogotovirus
| Thogotovirus | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Elektronenmikroskopische Aufnahme einer | ||||||||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomische Merkmale | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thogotovirus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||
|

Thogotovirus ist eine Gattung innerhalb der Virusfamilie der Orthomyxoviridae. Der erste bekannte Vertreter ist das Thogoto-Virus (englisch Thogoto virus, THOV; Spezies Thogotovirus thogotoense, früher Thogoto thogotovirus – ehemalige Typusart).[3][4]
Thogotoviren sind behüllte Viren mit einzelsträngiger RNA negativer Polarität als Genom. Das Genom der Thogotoviren hat typischerweise 6 oder 7 Segmente, d. h. ssRNA-Moleküle negativer Polarität. Thogotoviren verwenden als Arboviren Zecken als Vektor und können in Zellen von Zecken und Wirbeltieren vermehrt werden.[5]

Systematik
-
 Drei Virionen des Bourbon-Virus in der sphärischen Form
Drei Virionen des Bourbon-Virus in der sphärischen Form -
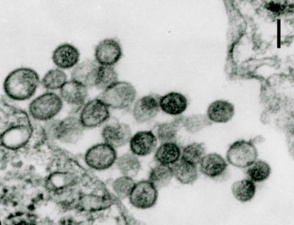 Upolu-Virus
Upolu-Virus -
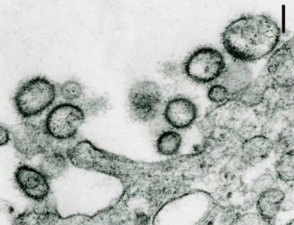 „Aransas-Bay-Virus“
„Aransas-Bay-Virus“
Das Thogoto-Virus wurde erstmals im Thogoto-Waldgebiet in Kenia isoliert und nach ihm benannt. Die Gattung Thogotovirus umfasst folgende Spezies und Subtypen/Isolate (Stand 7. Mai 2024):[3][4]
Gattung: Thogotovirus
- Spezies Thogotovirus bourbonense (abgetrennt von T. thogotoense) mit
- Bourbon-Virus (BOUV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus dhoriense mit
- Dhori-Virus Indian/1313/61 (DHOV)
- Batken-Virus (BKNV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus josense mit
- Jos-Virus (JOSV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus ozense mit
- Oz-Virus (OZV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus sinuense mit
- Sinu-Virus (SINUV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus thailandense mit
- Thailand tick thogotovirus (TT-THOV)
- Spezies Thogotovirus thogotoense (früher Thogoto thogotovirus, ehem. Typusspezies) mit
- Thogoto-Virus (THOV) inkl. SiAr 126
- Spezies Thogotovirus upoluense mit
- Upolu-Virus (UPOV)
- nicht klassifizierte Thogotoviren:[6]
- Spezies „Apis thogotovirus 1“
- Spezies „Aransas-Bay-Virus“ (englisch „Aransas Bay virus“, ABV)
- Spezies „Rondonia thogotovirus“
- Spezies „Soybean thrips thogotovirus 1“
- Spezies „Soybean thrips thogotovirus 2“
- Spezies „Tiliqua thogotovirus“
- …
Literatur
- Z. Hubálek, I. Rudolf, N. Nowotny: Arboviruses pathogenic for domestic and wild animals. In: Advances in virus research. Band 89, 2014, ISSN 1557-8399, S. 201–275, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800172-1.00005-7, PMID 24751197 (englisch).
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Akabane orthobunyavirus, EC 51, Berlin, Juli 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL #35)
- ↑ ICTV Master Species List 2018b.v2. MSL #34, März 2019
- ↑ a b ICTV: Taxonomy Browser.
- ↑ a b ICTV: Virus Metadata Resource (VMR).
- ↑ SIB: Thogotobirus. Auf: ViralZone (englisch).
- ↑ NCBI Taxonomy Browser: unclassified Thogotovirus












